Databases¶
InfluxDB¶
Characteristics - InfluxDB¶
In case of a time series data use case where you need to ingest data in a fast and efficient way you can use InfluxDB.
Information Model Requirements
Inserts using Events
The node after the root model in this case is of the type Event
 which represent a database table.
which represent a database table.
Inserts using Custom Data Types
Complex Variables
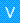 (ModuleA) represents Measurements
(ModuleA) represents MeasurementsVariables
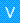 underneath within the complex variable (Temperature) represents Fields
underneath within the complex variable (Temperature) represents Fields
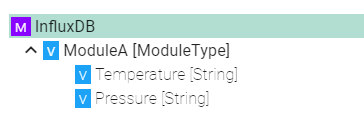
Arrays
 can be used to set use an index
can be used to set use an index
How to configure InfluxDB¶
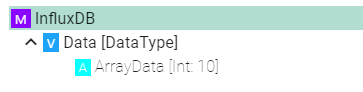
Select the root model node in the tree on the left.
Configure the InfluxDB.
Enter the URL to the database
Enter the database name
Enter the database username and password or select it from the Credentials Manager
Enter the Batch size - writes data in batches to minimize network overhead when writing data to InfluxDB
Enter the Flush interval (ms) - if data should be written every 10 seconds enter an flush interval of 10000ms
Event Configuration
Select the event node
Enable the checkbox to configure the event
Enter the measurement - if it differs from the event name
Enter tags - comma separated
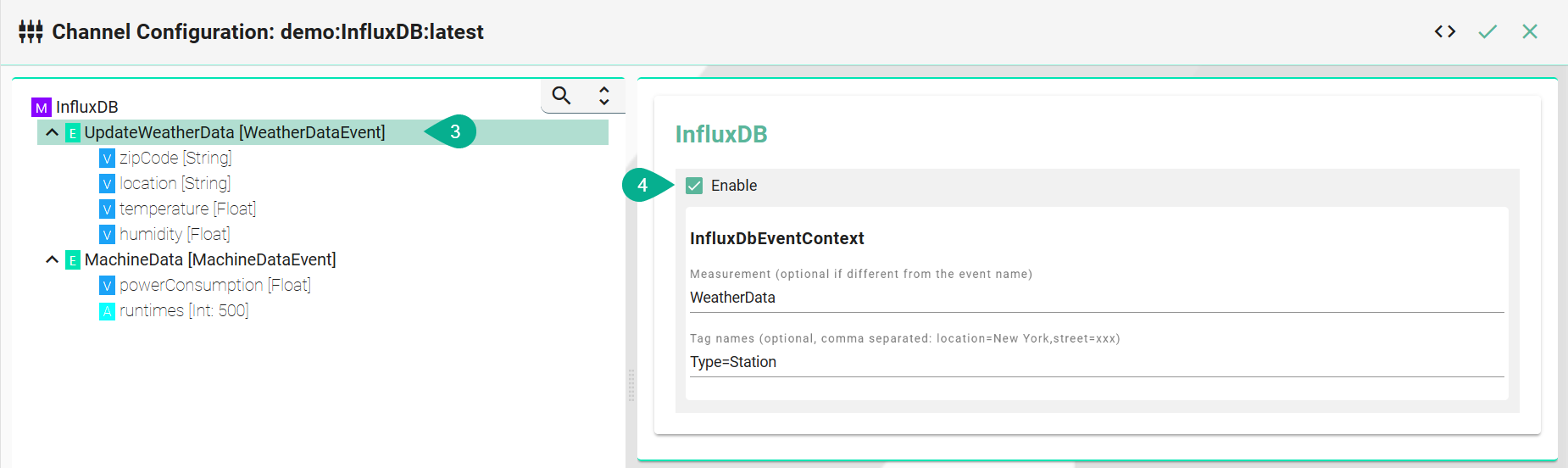
Configuration of tags
Select the variable which should be a tag
Enable Extended Configuration
Enter a name - if it differs from the variable name
Enable the checkbox isTag
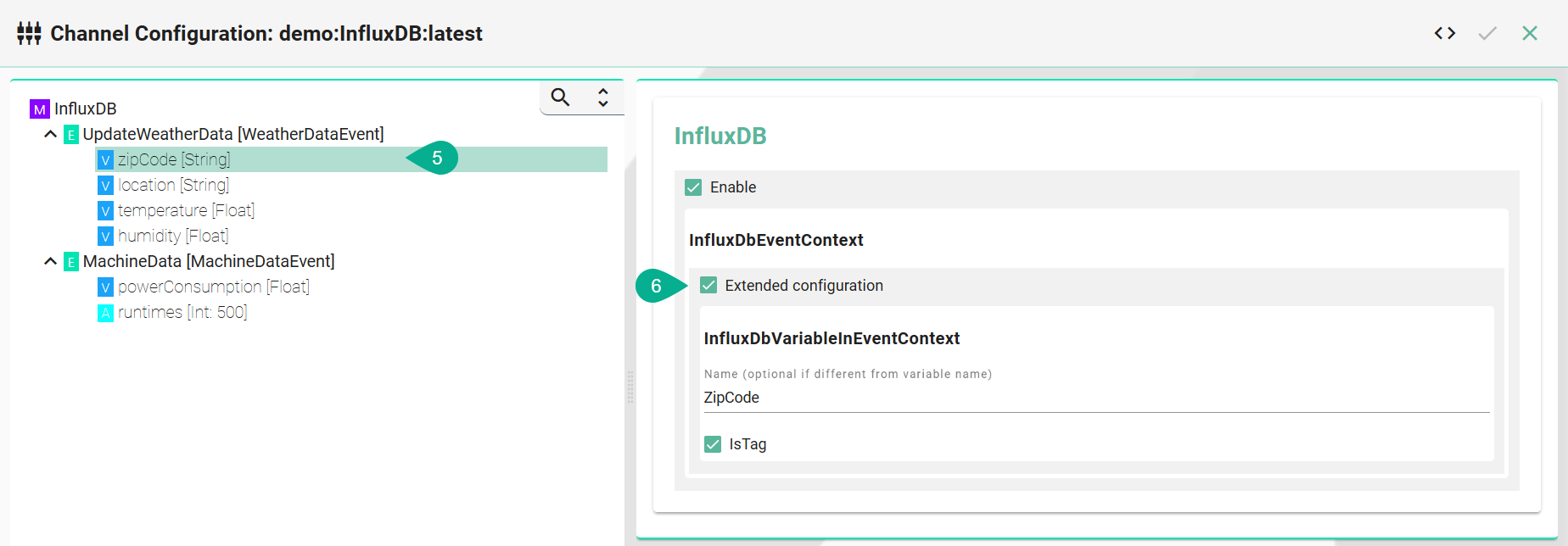
Configuration of fields
Select the variable which should be a field
Enable Extended Configuration
Enter a name - if it differs from the variable name
Leave the checkbox isTag disabled
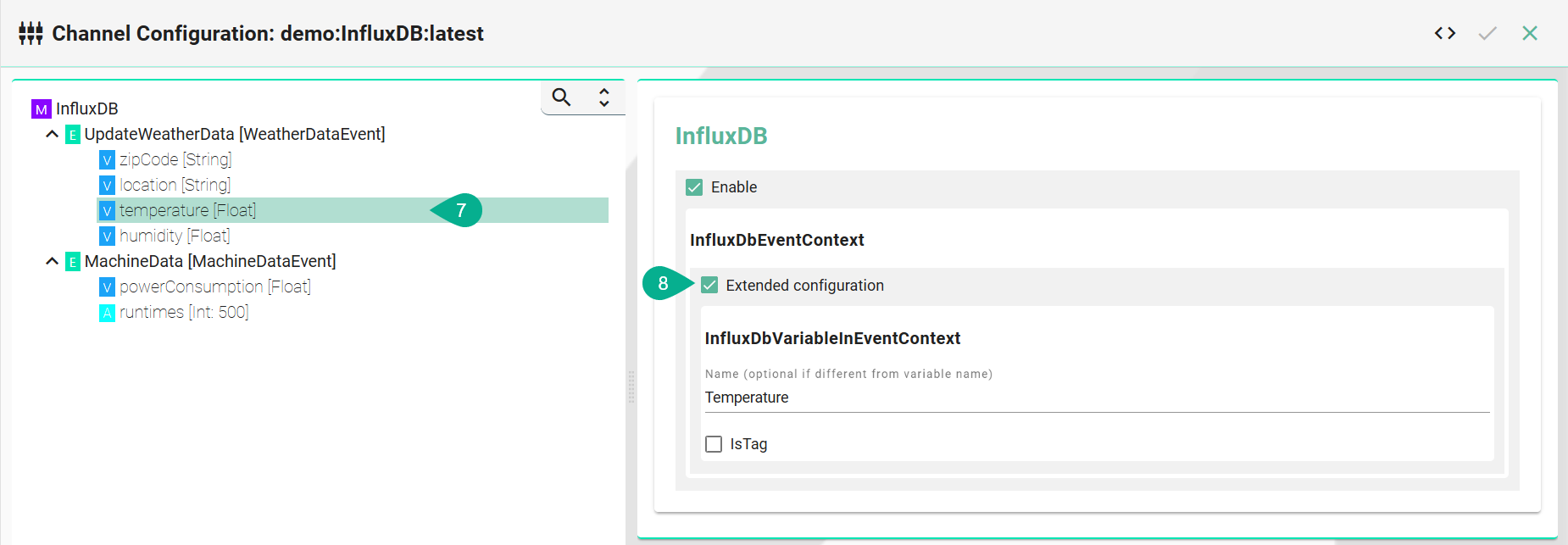
Array Configuration
Select the Array
To configure the Array select Extended Configuration
(Optional) Enter a index name
(Optional) Enter a field names if the event node name differs from the actual name in InfluxDB.
(Optional) Enter tags separated by commas e.g., (location=NewYork, street=xxx)
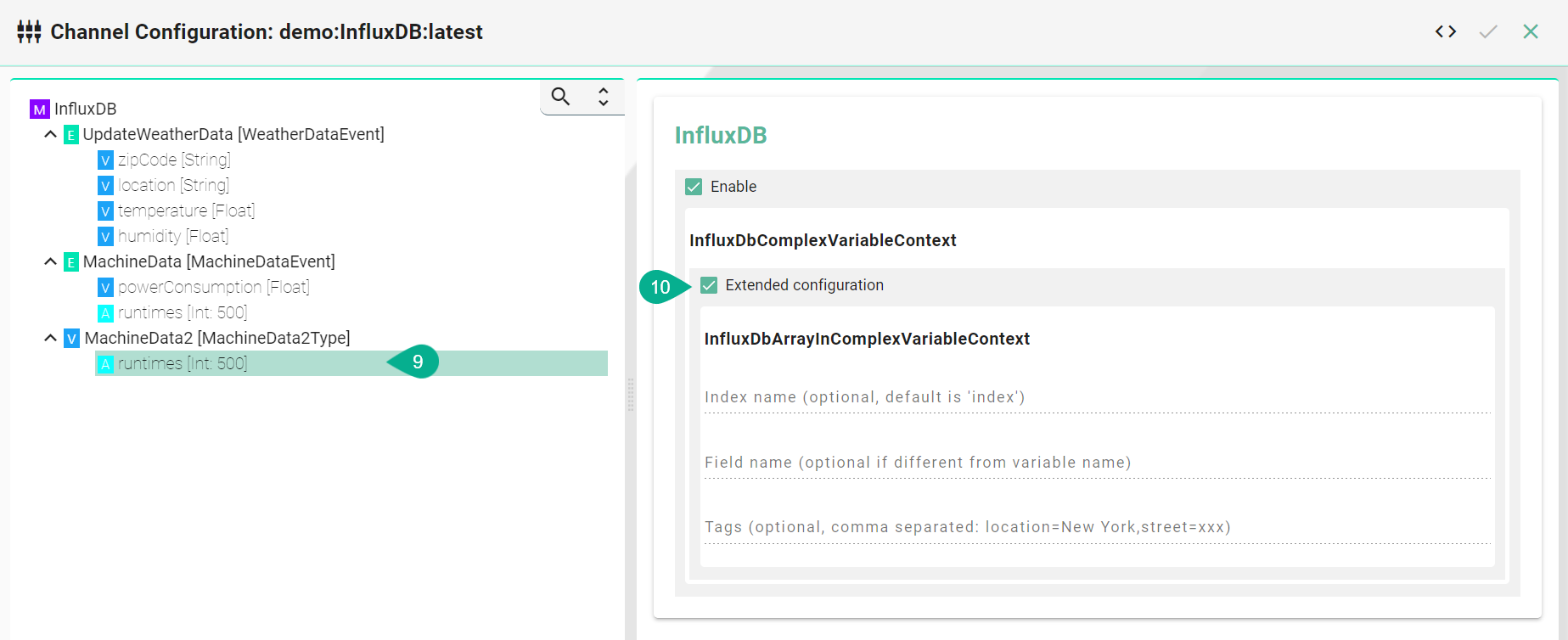
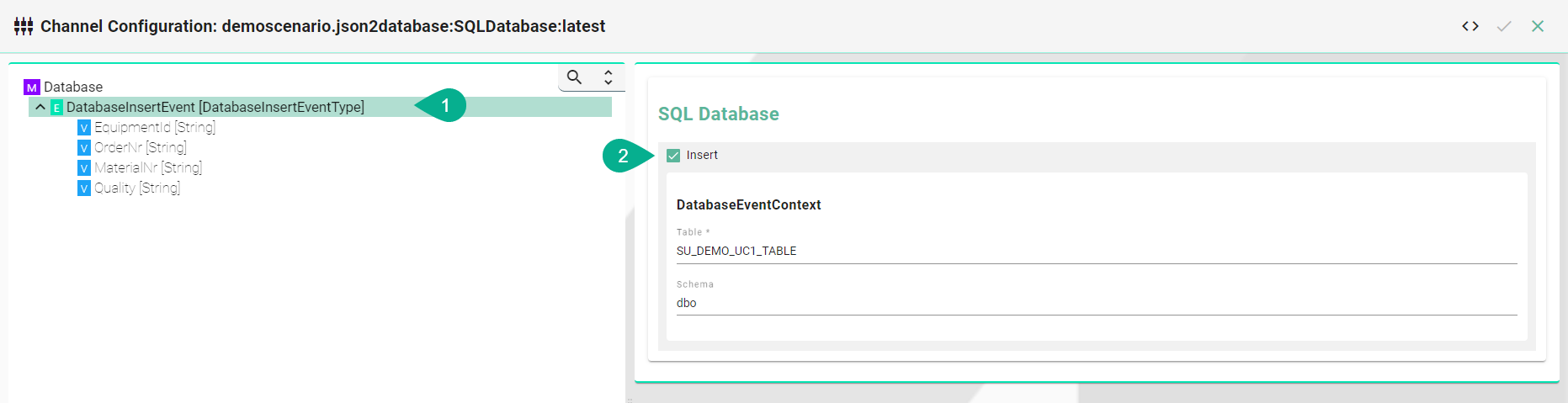
SQL Database¶
Characteristics - SQL Database¶
The SQL Channel can be configured for the following two scenarios:
Inserting data
Updating data
Retrieving data
When inserting values into the database please note that “infinity” values are converted automatically into “null” values.
Information Model Requirements
Insert/Update
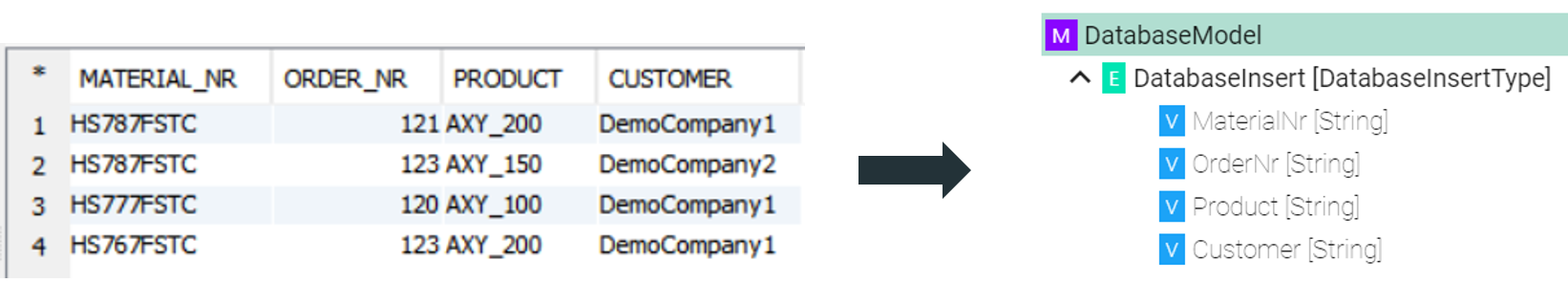
The node after the root model node must be of type Event
 which represent a database table.
which represent a database table.In case of relational databases: Tables which are dependent on each other require a List
 .
.Columns of databases are represented by Variables
 .
.
Select
The Command
 defines that after a request is made, a reply with a result is expected.
defines that after a request is made, a reply with a result is expected.Parameters
 within a Command represent a collection of query parameter - query parameters are defined as Variables
within a Command represent a collection of query parameter - query parameters are defined as Variables  .
.Reply
 within a Command represents the result of the Command - results are defined as Variables
within a Command represents the result of the Command - results are defined as Variables 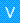 .
.
How to configure the SQL-Database¶
Select the root model node in the tree on the left.
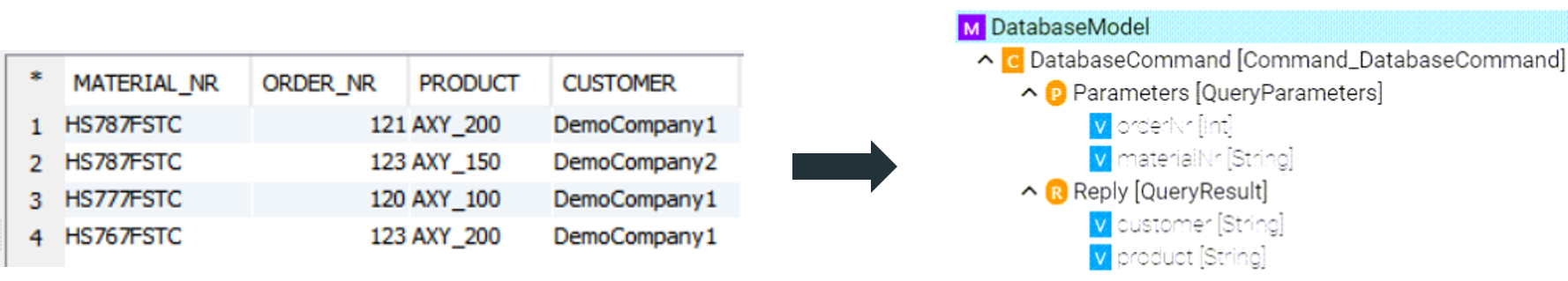
Configure the database connection
Select the database type.
Specify a reconnection interval.
Enter the database connection url for the specific database type.
DB2:
jdbc:db2:server:port/databaseHSQLDB:
jdbc:hsqldb:file:databaseFileName;propertiesORACLE:
jdbc:oracle:thin:prodHost:port:sidPostgreSQL:
jdbc:postgresql://host:port/databaseSQLServer:
jdbc:sqlserver://[serverName[\instanceName][:portNumber]][;property=value[;property=value]]MariaDB:
jdbc:(mysql|mariadb):[replication:|loadbalance:|sequential:|aurora:]//<host>[:<portnumber>]/[database][?<key1>=<value1>[&<key2>=<value2>]]
Enter the database username and password or select it from the Credentials Manager.
Property |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Type |
Type of the database |
|
ReconnectInterval |
Time to reconnect if connection fails |
|
JdbcUrl |
Url to connect to database |
|
Username and password |
Credentials of the database |
Note
The configuration of specific information model nodes differs whether you want to perform an insert or an select statement on the database. Inserting data into the database requires an event node whereas selecting data requires a command node in the Information Model.
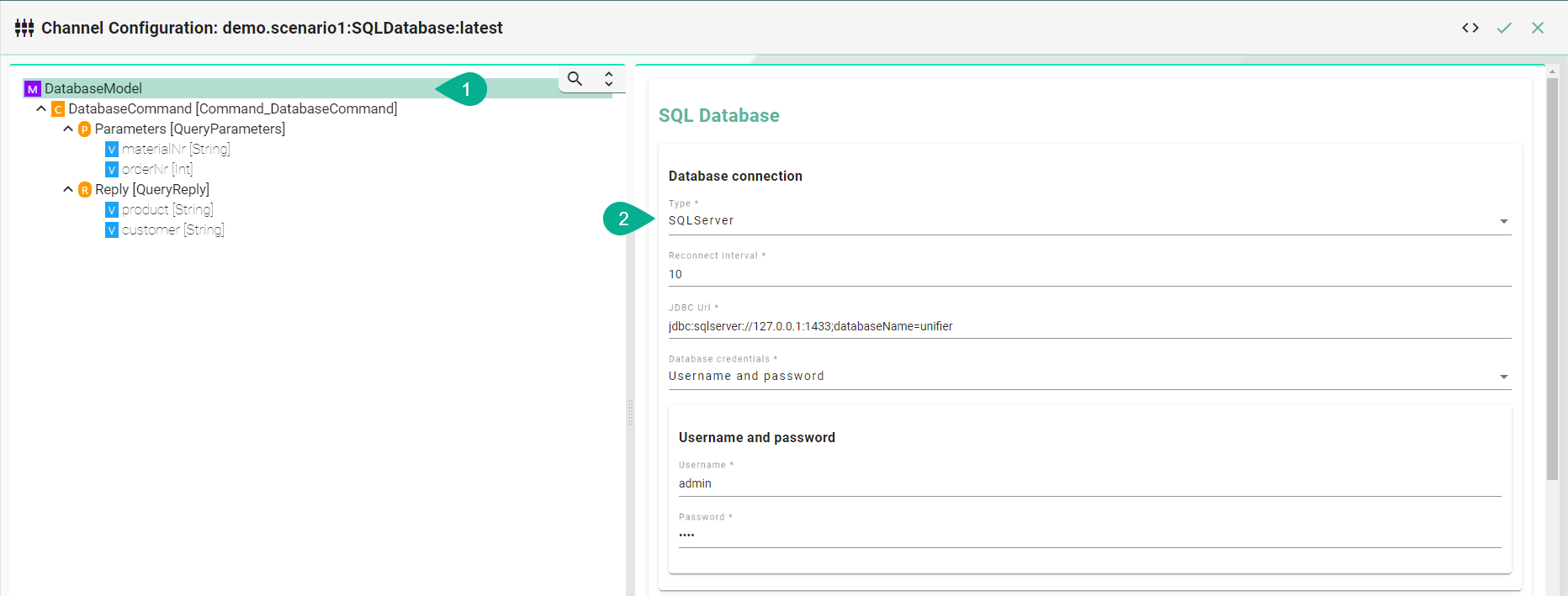
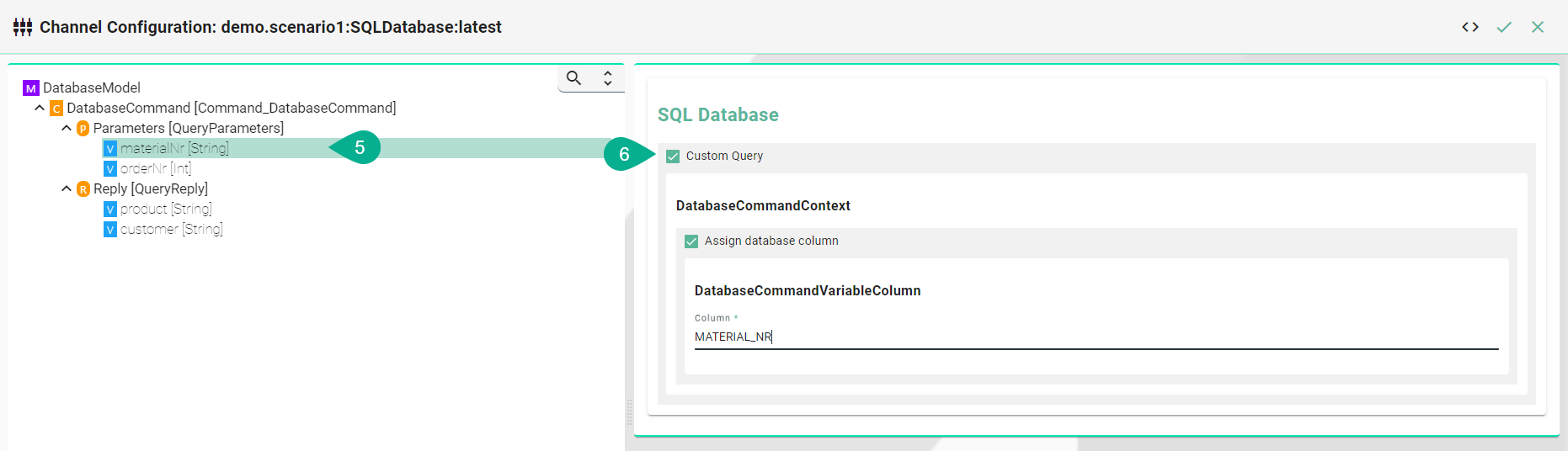
Select Statement
Select the command node in the tree on the left.
Check the custom query checkbox and enter the sql query.
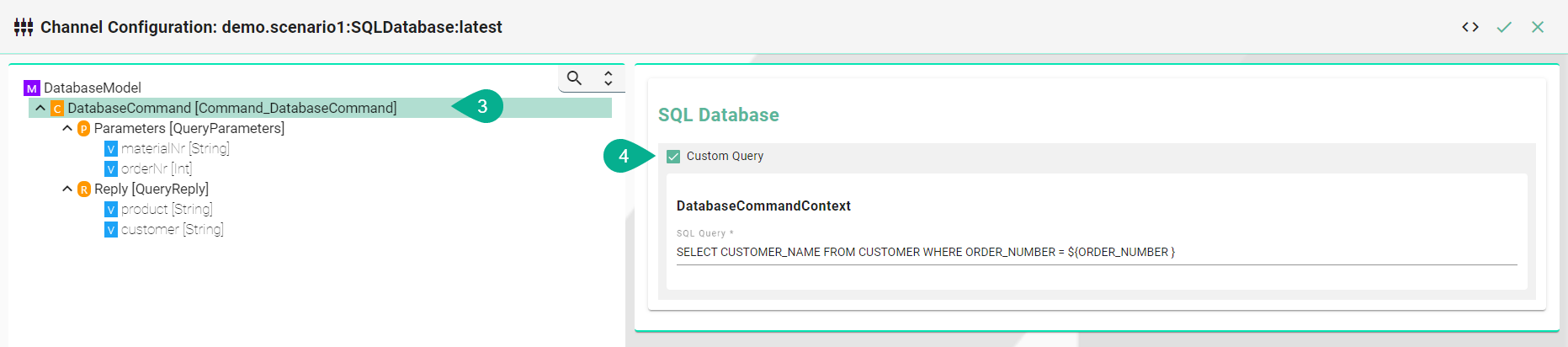
Each variable under Parameters and Reply needs to be assigned to a database column. Select the variable node under Parameters and in the tree select what needs to be configured.
Check the assign database column checkbox and enter the column name as it is defined in the used database.
Insert Statement
Select the event node in the tree on the left.
Check the insert checkbox and enter the table name. If required enter a schema name.