InfluxDB v1¶
Characteristics - InfluxDB v1¶
InfluxDB v1 is the initial version of the high-performance time-series database designed for time-stamped data storage and real-time analytics, for more information visit the influxdata website.
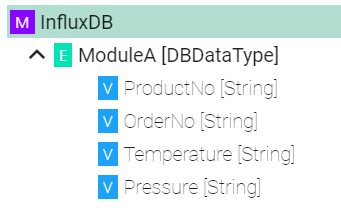
Information Model Requirements
Measurements are represented by Event
 and Complex Variables
and Complex Variables 
Tags and Time are as well represented by Variables
 but they have to be specifically configured (see below Tags configuration and Time configuration)
but they have to be specifically configured (see below Tags configuration and Time configuration)

How to configure InfluxDB v1¶
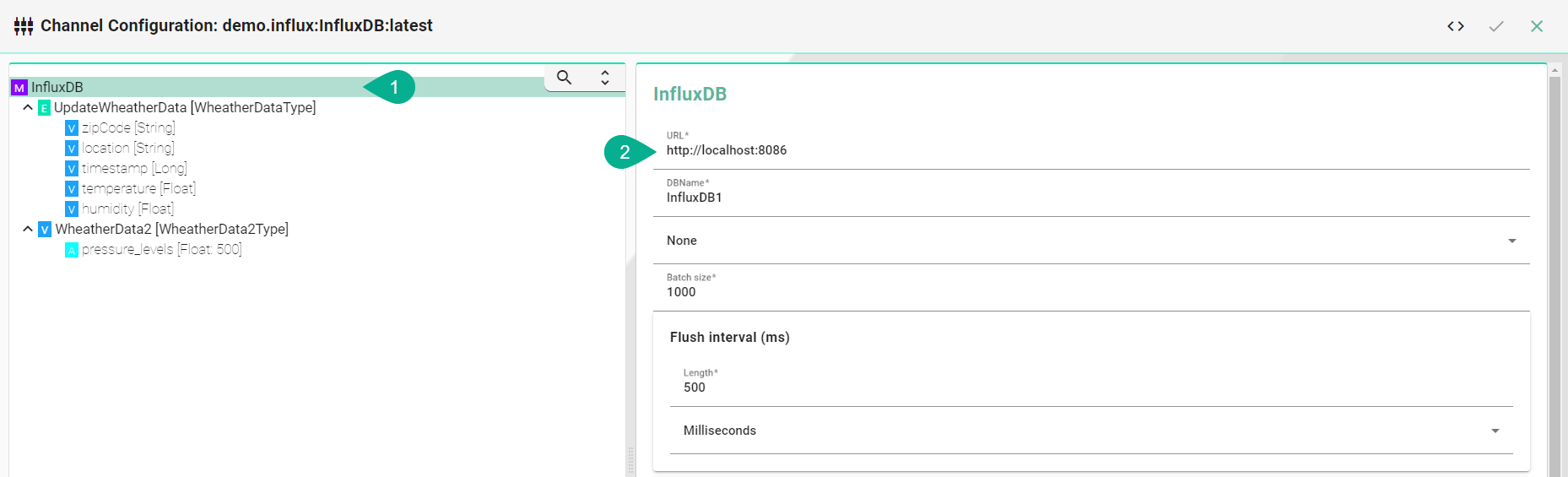
Select the root model node in the tree on the left.
Configure the InfluxDB.
Enter the URL to the database
Enter the Database name
Enter the database Username and Password or select it from the Credentials Manager
Enter the Batch size - writes data in batches to minimize network overhead when writing data to InfluxDB
Enter the Flush interval and select the Unit (Please note that too short intervalls might cause data loss!)
Event Configuration
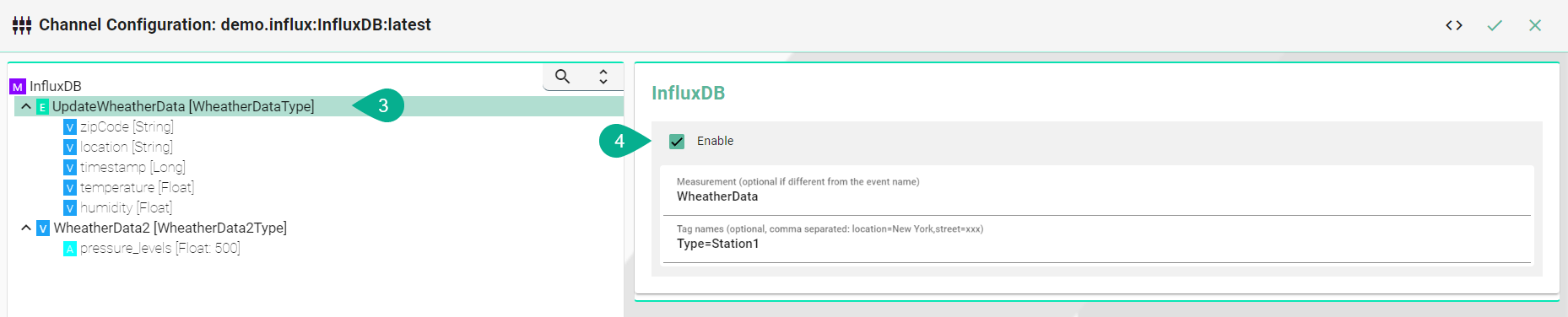
Select the event node
Enable the checkbox to configure the event
Enter the Measurement - if it differs from the event name
Enter Tags - comma separated
Tags are metadata for the data. They’re made up of key-value pairs, and they describe attributes of the data that don’t change every time the data point is recorded. To configure a variable as a tag follow the steps below:
Select the variable which should be a Tag
Enable Extended configuration
Select Tag from the drop-down menu
Enter a Name - if it differs from the variable name

Configuration of Fields
Fields represent the actual data stored and consist of key-value pairs. Unlike tags, fields aren’t indexed. Variables not explicitly configured are automatically recognized as fields by the InfluxDB Channel.
If the field name should differ from the variable name in the Information Model, follow the steps below:
Select the variable which should be a field
Enable Extended configuration
Select Field from the drop-down menu
Enter a Name - if it differs from the variable name

Configuration of Time
Timestamps indicates when a data point occurred and, in combination with its tag set, uniquely identifies that data point in a series. To configure a variable as a time follow the steps below:
Select the variable which should be a time
Enable Extended configuration
Select Time from the drop-down menu
Select the Precision (Only for variables of type Int or Long)
Enter a Formatter (This is required if time is provided as a String)

Array Configuration
Select the Array
To configure the Array select Extended Configuration
(Optional) Enter an Index name
(Optional) Enter a Field name if the event node name differs from the actual name in InfluxDB.
(Optional) Enter Tags separated by commas e.g., (location=NewYork, street=xxx)

Description of configuration properties:
Property |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
URL |
Database URL and port |
|
DB Name |
Database name |
|
Credentials |
Database credentials |
|
Batch size |
Data written in batches |
|
Flush interval |
Delay between data flushes in milliseconds, at most batch size records are sent during flush |
|
Measurement |
Name of the measurement stored in influxdb |
|
Tag names |
Optional tag to be added to the measurement |
|
