Information Models
What are Information Models
Within the SMARTUNIFIER an Information Model describes the communication related data that is available for a device or IT system. One device or one IT system therefore is represented by one Information Model. An Information Model consists of so-called Node Types. Information Models are built up in a hierarchical tree structure, i.e., elements within the Information Model can contain further elements. This is required to model the data structure of devices as naturally as possible.
Before starting to model the data structure of e.g., an equipment or IT-System the overall use case should be known. Typically, each equipment or IT-system that is going to be integrated gets its own Information Model. If there are equipments and IT-systems of the same type, you can use one common Information Model.
How to create a new Information Model
Follow the steps described below to create an Information Model:
Select the SMARTUNIFIER Information Model Perspective (1).
You are presented with the following screen containing a list view of existing Information Models.
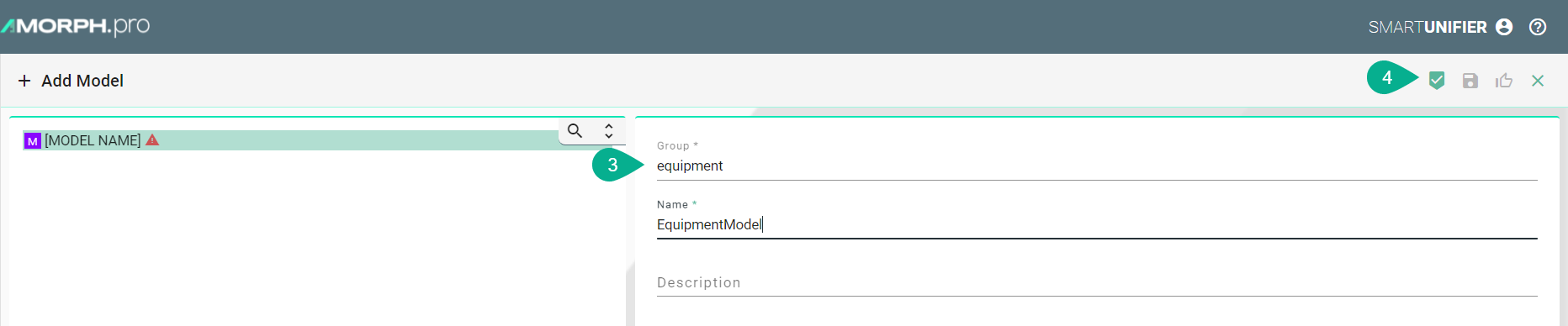
In order to add a new Information Model, select the “Add Model“ button at the top right corner (2).

On the following screen provide the following mandatory information: Group and Name (3).
The “Apply” button at the top right corner is enabled after all mandatory fields are filled in. Click the button to generate a new Information Model (4).
The newly created Information Model is now visible as a node on the left side of the screen.
After the root model node is created, a new Information Model can be built up using definition types.
Perform a right click on the root model node and select “Add Node” (5). Select a Definition Type from the dialog (6).

Node Types
Depending on the use case and the Communication Channels you need to choose the proper Node Type. Model node types are elements within an Information Model, like variables, properties, events, commands and also collections such as arrays and lists. Each model node type has a Data Type that defines whether the model node type is a predefined data (e.g.: String, Int, Boolean, etc.) type or a custom data type.
Supported Model Node Types:
Data Types
There are two kinds of Data Types:
Predefined Types e.g., String, Integer, Boolean and more. (Note: Only available for the definition types - Variables, Properties, Arrays, Lists)
Custom Types
How to create a Variable as a Simple Type
Add a new Variable, enter an ID and select a primary data type for the Data Type e.g., “String” (1)

Type |
Definition |
|---|---|
Boolean |
true or false |
Byte |
8 bit signed value (-27 to 27-1) |
Int |
32 bit signed value (-231 to 231-1) |
String |
Sequence of characters |
Char |
16 bit unsigned Unicode character (0 to 216-1) |
Double |
64 bit IEEE 754 double-precision float |
Float |
32 bit IEEE 754 single-precision float |
Long |
64 bit signed value (-263 to 263-1) |
Short |
16-bit signed integer |
Array |
Mutable, indexed collections of values. |
List |
Class for immutable linked lists representing ordered collections of elements. |
LocalDate |
Immutable date-time object that represents a date, often viewed as year-month-day. |
LocalDateTime |
Immutable date-time object that represents a date-time, often viewed as year-month-day-hour-minute-second. |
LocalTime |
Immutable date-time object that represents a time, often viewed as hour-minute-second. |
OffsetDateTime |
Immutable representation of a date-time with an offset. |
How to create a Variable as a Custom Type
Add a new Variable, enter an ID and enter a custom name for the Data Type e.g., “MyFirstComplexVariableType” (1)
Select the Custom Variable - “MyFirstComplexVariableType” - and add a new Variable underneath it (2)
Note
Model Node Types with custom data types can be easily duplicated throughout the Information Model by selecting the same custom data type for a new model node type.

Data Types for Properties, Arrays and Lists can be defined as shown above for Variables.
Information Model Structure
The structure of an Information Model depends upon the used Communication Channel in the integraton. Communication Channels can be categorized into data-driven and event-driven communication.
Event-driven refers to an integration triggered by an event that takes place in a system e.g., goods receipt. This event triggers a Rule with in the Mapping of SMARTUNIFIER.
Data-driven, on the other hand, is spurred by a change in the actual data in a system.
SMARTUNIFIER also considers command-driven integration were an event takes place in a system and immediatley expects an reply from another system. This is in contrast to the event-driven integration were no reply is expected.
The table below provides some use case examples with its required Information Model structure.
Use Cases |
Description |
Communication Channel |
Information Model Structure |
|---|---|---|---|
Data driven |
Retrieving data from OPC-UA Server |
OPC-UA Client |
Simple Data Type Variables under the Root node |
Custom Data Type Variables under the Root node |
|||
Event driven |
Posting data on MQTT Broker |
MQTT client |
Event under the Root node |
· Simple Data Type Variables under the Event node |
|||
· Custom Data Type Variables under the Event node |
|||
· Lists under the Event node |
|||
Command driven |
Executing Select request on a database with parameters |
SQL Database |
Command under the Root node |
· Simple Data Type Variables under the Command Parameters |
|||
· Simple Data Type Variables under the Command Reply |
What Information Model structure is required for each communication channel is described in the chapter Communication Channels.
Data structures can be imported by using extensions which is especially convenient when dealing with complex structures with a lot of variables: - OpcUa Model Import: Data structures can be imported form a OPC UA server - JSON Model Import: JSON structures can be imported directly