SECS/GEM
Characteristics - SECS/GEM
The SECS/GEM is the semiconductor’s equipment interface protocol for equipment-to-host data communications. In an automated fab, the interface can start and stop equipment processing, collect measurement data, change variables and select recipes for products. To learn more about the standard visit the SECS/GEM section in Wikipedia website.
Information Model Requirements
The first Node after the root node
 can be of type Event
can be of type Event 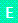 , Command
, Command  or Variable
or Variable 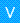
The following Node Types can be used under the Event Node:
Variables
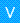 with a Simple Data Type represents the key-value pairs.
with a Simple Data Type represents the key-value pairs.Variables
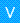 with a Custom Data Type represent objects that can contain key-value pairs.
with a Custom Data Type represent objects that can contain key-value pairs.

Configuration - SECS/GEM Client
Select Secs Gem Client as Channel Type.
Click the Configure button.
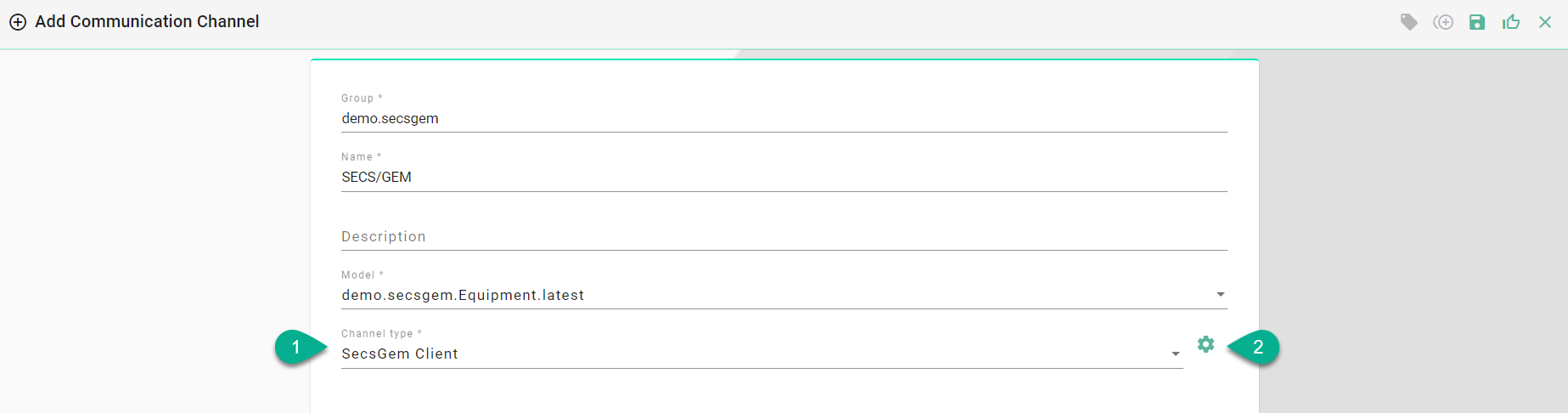
Make sure the root model node is selected to configure the SECS/GEM Client
Enter the device configuration:
input the equipment-to-host Ip address
type in the TCP Port for the communication
input the Device Id
Enter the Data Formats
Input CEID - format for event Ids
Enter RPTID - format for report Ids
Input ALID - format for alarm Ids
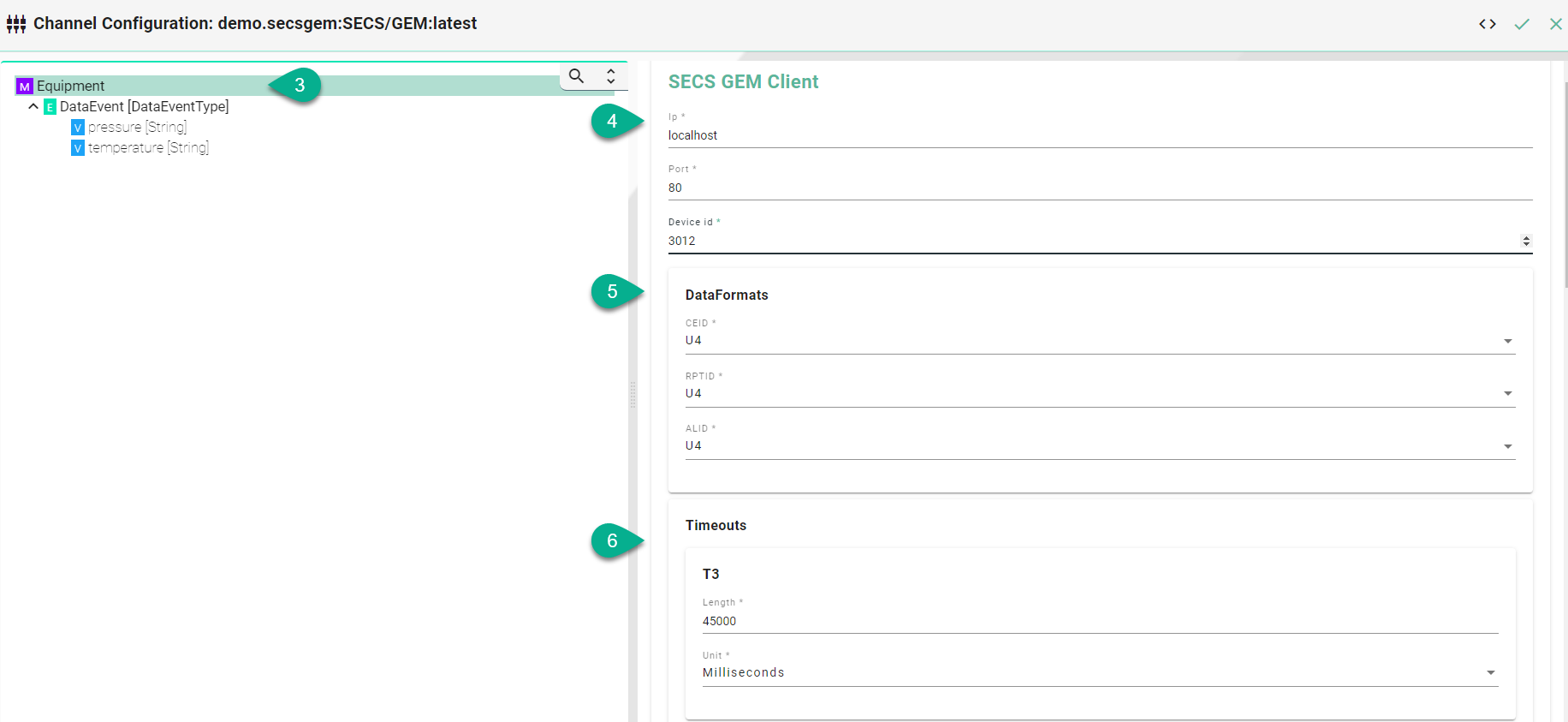
Input timeout for:
T3 - Reply Timeout in the HSMS protocol.
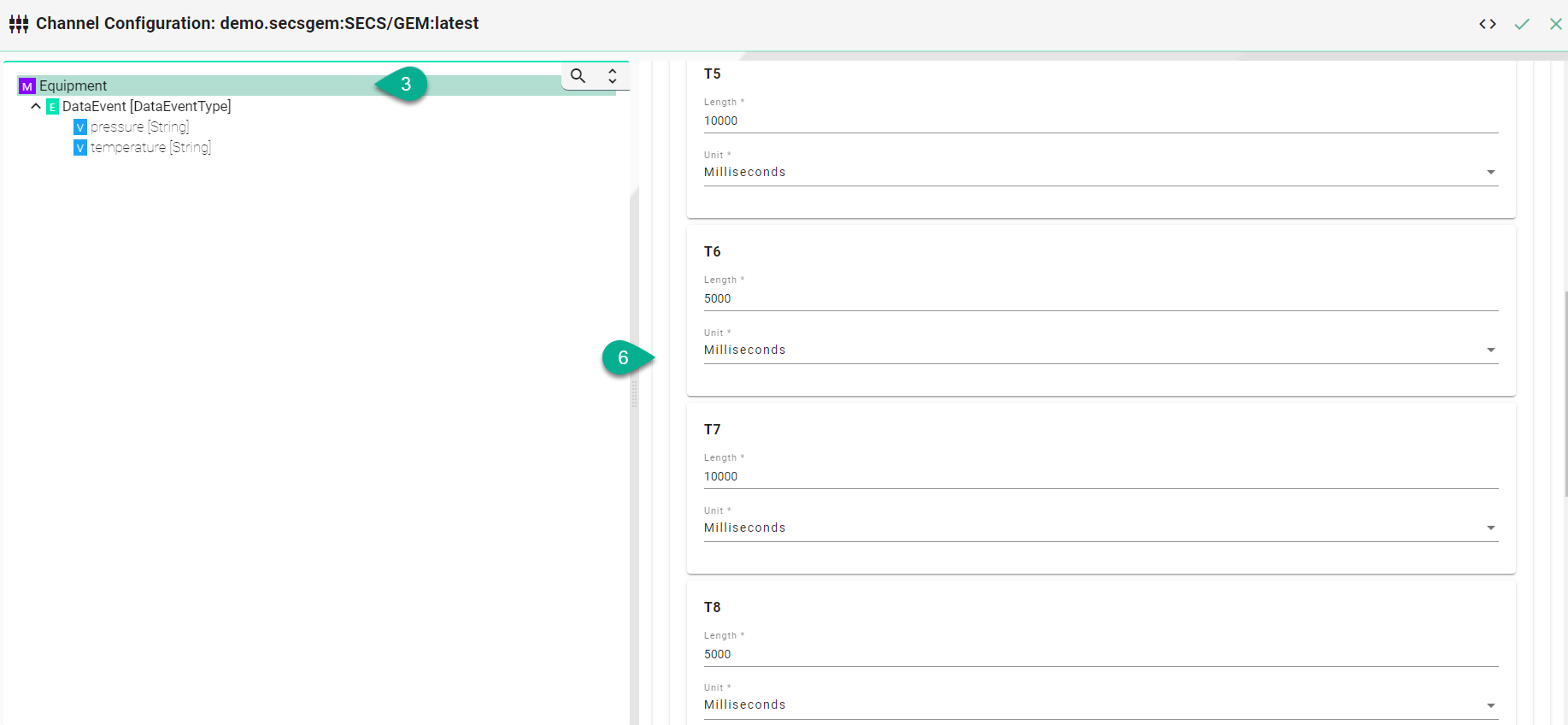
T5 - Connect Separation Timeout in the HSMS protocol used to prevent excessive TCP/IP connect activity by providing a minimum time between the breaking, by an entity, of a TCP/IP connection or a failed attempt to establish one, and the attempt, by that same entity, to initiate a new TCP/IP connection.
T6 - Control Timeout in the HSMS protocol which defines the maximum time an HSMS control transaction can remain open before a communications failure is considered to have occurred. A transaction is considered open from the time the initiator sends the required request message until the response message is received.
T7 - Connection Idle Timeout in the HSMS protocol which defines the maximum amount of time which may transpire between the formation of a TCP/IP connection and the use of that connection for HSMS communications before a communications failure is considered to have occurred.
T8 - Network Intercharacter Timeout in the HSMS protocol which defines the maximum amount of time which may transpire between the receipt of any two successive bytes of a complete HSMS message before a communications failure is considered to have occurred.
Select the logging type for the required Node Types:
Check the Enable box
Check the Log Data box
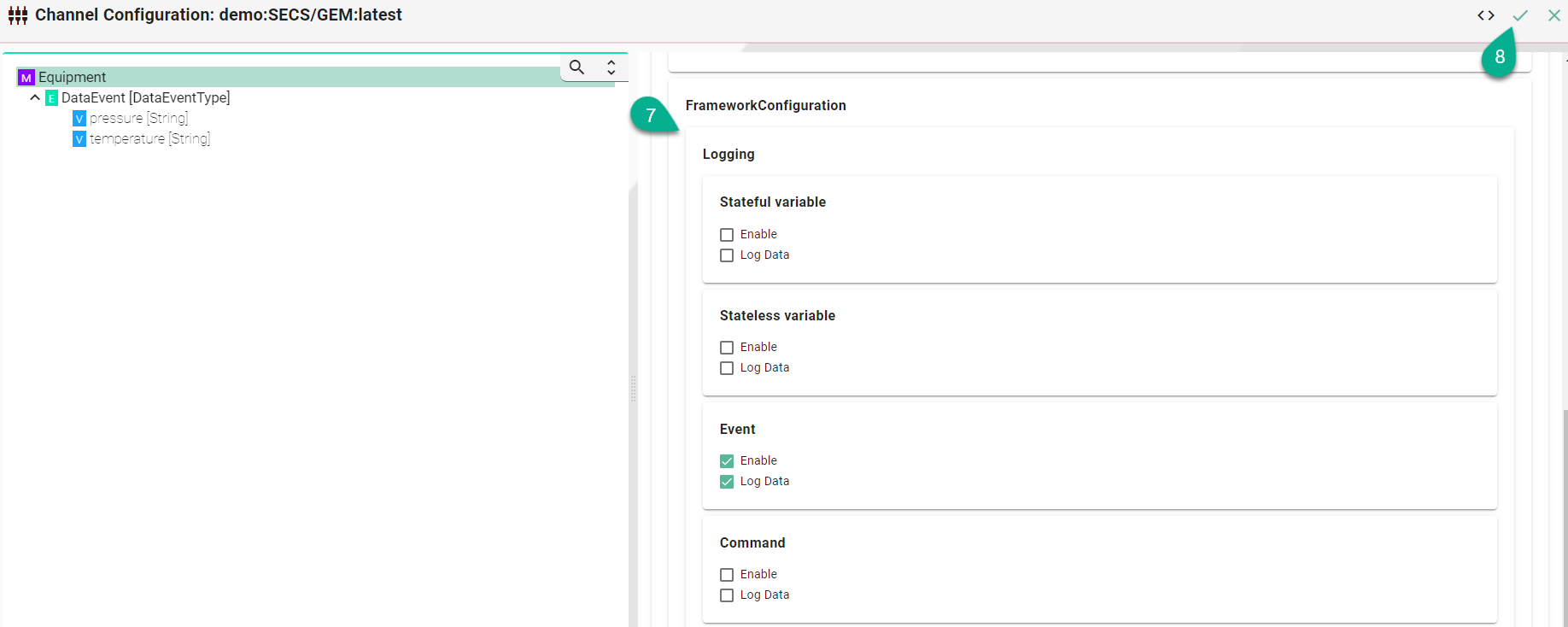
Click on the Apply button
Select the Event node to configure the event context
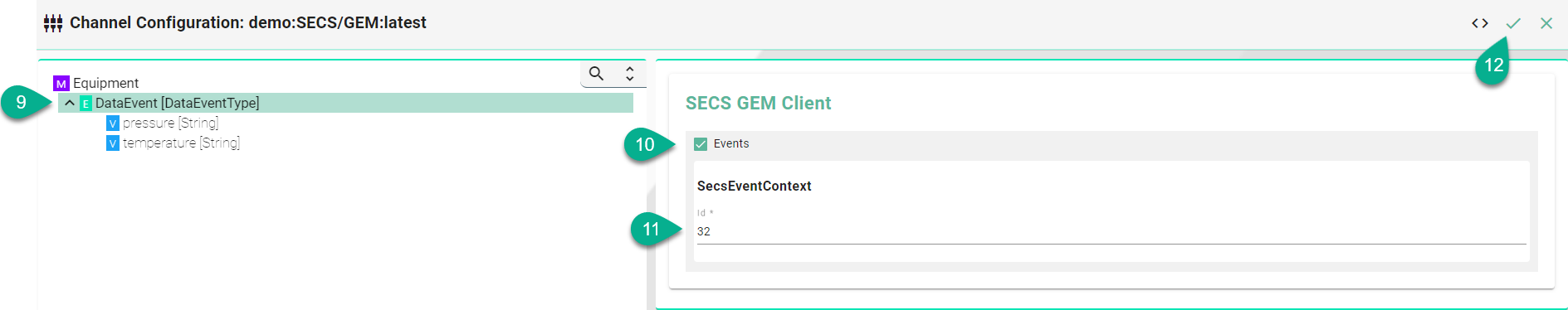
Click to check the Events box
Enter the event context Id which will trigger the event in the Information Model
Click on the Apply button
Select the variable in the tree

Click to check the variables box and configure the Secs variable context
select the variable Type
enter the variable Id
click the Is SV box to check if the variable is a SV
input the variable Name
Description of configuration properties:
Property |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Ip |
IP address of the Equipment |
|
Port |
TCP port for the communication |
|
Device Id |
Id of the equipment |
|
CEID |
Format for event Ids |
|
RPTID |
Format for report Ids |
|
ALID |
Format for alarm Ids |
|
Timeouts |
Time interval the connection times out in milliseconds |
|
T3 |
Reply timeout in the HSMS protocol |
|
T5 |
Connect Separation Timeout in the HSMS protocol |
|
T6 |
Control Timeout in the HSMS protocol |
|
T7 |
Connection Idle Timeout in the HSMS protocol |
|
T8 |
Network Intercharacter Timeout in the HSMS protocol |
|
Id |
Id of the equipment event which will trigger the event |
|
Type |
Type of variable |
|
Id |
Variable Id |
|
Type |
Commands - Type of the message |
|
Id |
Commands Id |
|
RCMD |
Name of command if it is different from the command Id |
|